Showing posts with label SQL Server 2008. Show all posts
Showing posts with label SQL Server 2008. Show all posts
Wednesday, January 08, 2014
SQL Server 2012: SELECT Machine Name, Server Name, Edition, Product Level, Product Version, Licence Type
Description
This post shows how to SELECT property information for a SQL Server.
Solution
The SELECT statement below retrieves Machine Name, Server Name, Edition, Product Level, Product Version, and License Type.
SELECT
SERVERPROPERTY('MACHINENAME') as [Machine Name],
SERVERPROPERTY('SERVERNAME') as [Server Name],
SERVERPROPERTY('EDITION') as [Edition],
SERVERPROPERTY('PRODUCTLEVEL') as [Product Level] ,
SERVERPROPERTY('PRODUCTVERSION') as [Product Version],
SERVERPROPERTY('LICENSETYPE') as [License Type]
The results of the query are shown below.
References
MSDN (2014). SERVERPROPERTY (Transact-SQL). Retrieved January 8, 2014 from http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms174396.aspx
Tuesday, January 07, 2014
How to Associate SQL Server Login with Existing Database User
Description
Sometimes a SQL Server Login is created and corresponding Database User is created at the same time. However, sometimes the Database User is not associated with a SQL Server Login and needs to be. For example, this could happen during an database environment migration or if when the Active Directory User Account associated with SQL Server Login is deleted and a new one is created.
Solution
The steps below can be used to lookup database principals and then associate a Login with a User.
1. Run the SELECT query below to view all database principals, including:
- DATABASE_ROLE
- SQL_USER
- WINDOWS_USER
SELECT * FROM sys.database_principals
2. Run ALTER USER query below to alter the database user and associate a login with it. In the example below, a Windows Login is being associated with a database user.
ALTER USER "DOMAIN\Username"
WITH
LOGIN = "DOMAIN\Username"
(Microsoft TechNet, 2014)
References
Bertrand, A. (November, 2013). Script to Set the SQL Server Database Default Schema For All Users. Retrieved January 7, 2014 from
http://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/3098/script-to-set-the-sql-server-database-default-schema-for-all-users/
Microsoft TechNet (2014). ALTER USER (Transact-SQL). Retrieved January 7, 2014 from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms176060.aspx
Tharaka MTR (May, 2013). How to Fix Orphaned SQL Users. Retrieved January 7, 2014 from http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/594134/How-to-Fix-Orphaned-SQL-Users
Labels:
SQL Server,
SQL Server 2008,
SQL Server 2008 R2,
SQL Server 2012,
T-SQL
Sunday, August 11, 2013
Error: SQL Server: Unable to Shrink Transaction Log, "Could not locate file for database..."
Description
You attempt to shrink a transaction log file associated with a SQL Server database, but you receive in error:
"Could not locate file 'Transaction Log Name' for database
'Database Name' in sys.database_files. The file either does not exist, or was dropped."
Solution
1) Run SP_HelpFile to get the correct name of the transaction log file.
USE Database Name
EXEC sp_helpfile
(TechNet, 2013)
This will return the following information about the database files, including the associated transation log(s): Name, FileId, FileName, FileGroup, Size, MaxSize, Growth, Usage
2) Run the Transact-SQL statement again, using the correct Transaction Log Name. You can find this in the Name column of the SP_HelpFile query results set.
USE [Database Name]
GO
ALTER DATABASE Database Name SET RECOVERY SIMPLE WITH NO_WAIT
DBCC SHRINKFILE(Transaction Log Name, 1)
ALTER DATABASE Database Name SET RECOVERY FULL WITH NO_WAIT
GO
(TechNet, 2013)
3) Verify that there are configured, scheduled, and enabled SQL Server Backup jobs in place for:
a) Full Database Backup
b) Transaction Log Backup *Important for Full Recovery Model*
Reference
TechNet (2013). Backup Under the Full Recovery Model. Retrieved August 11, 2013 from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms190217%28v=sql.105%29.aspx
TechNet (2013). DBCC SHRINKFILE (Transact-SQL). Retrieved August 11, 2013 from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms189493.aspx
TechNet (2013). Recovery Models and Transaction Log Management. Retrieved August 11, 2013 from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms366344%28v=sql.105%29.aspx
TechNet (2013). sp_helpfile. Retrieved August 11, 2013 from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa933456%28v=sql.80%29.aspx
Labels:
DBA,
SQL Server,
SQL Server 2008,
SQL Server 2008 R2,
SQL Server 2012
Monday, August 29, 2011
Error: Microsoft SQL Server: Cannot connect to (local)
Description
Error when attempting to log into SQL Server Management Studio: "Cannot connect to (local)."
Solution
As the error message indicates, the SQL Server is not accessible. The issue may be caused by one of the following:
1) Issue with Server Connection Configuration
Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server > Configuration Tools > SQL Server Configuration Manager
Verify the correct protocols are configured (this will vary based on type of environment). Refer to Microsoft TechNet article, Choosing a Network Protocol, for further assistance with this topic.
2) Issue with Service Account Authentication
Start > Administrative Tools > Services
Verify that the SQL Server (MSSQLServer) Service is running. If it is not running, try to start it. Make sure the Service Account credentials are properly configured and that the account is not locked out.
References
Microsoft TechNet (August, 2011). Choosing a Network Protocol. Retrieved August 29, 2011 from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms187892.aspx.
Error when attempting to log into SQL Server Management Studio: "Cannot connect to (local)."
Solution
As the error message indicates, the SQL Server is not accessible. The issue may be caused by one of the following:
1) Issue with Server Connection Configuration
Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server > Configuration Tools > SQL Server Configuration Manager
Verify the correct protocols are configured (this will vary based on type of environment). Refer to Microsoft TechNet article, Choosing a Network Protocol, for further assistance with this topic.
2) Issue with Service Account Authentication
Start > Administrative Tools > Services
Verify that the SQL Server (MSSQLServer) Service is running. If it is not running, try to start it. Make sure the Service Account credentials are properly configured and that the account is not locked out.
References
Microsoft TechNet (August, 2011). Choosing a Network Protocol. Retrieved August 29, 2011 from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms187892.aspx.
Thursday, December 02, 2010
SQL Server 2008: Edit Top 200 Rows
SQL Server 2005 and earlier versions had an Open Table command available when you right-click a table. This allows you to open the table and make edits to fields. In SQL Server 2008, the Open Table command is replaced with the Edit Top Rows command. The default for this is 200, which of course, is obnoxious.
 To change this setting, follow these steps from SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS):
To change this setting, follow these steps from SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS):

After modifying the setting, you will see that the menu is updated accordingly.
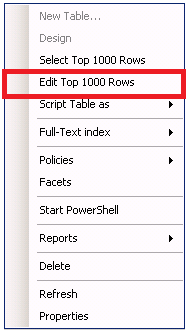
 To change this setting, follow these steps from SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS):
To change this setting, follow these steps from SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS):- Tools > Options (This opens the General Scripting Options Dialog Box)
- SQL Server Object Explorer > Commands
- Table and View Options: Value for Edit Top Rows command (Change this value)

After modifying the setting, you will see that the menu is updated accordingly.

Reference
Microsoft (2010). Options (SQL Server Object Explorer/Commands). Retrieved December 2, 2010 from http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc280381.aspx.
Monday, May 18, 2009
SQL Server 2008: A Must Do Configuration for Resource Governor
Over the past few months, I have been upgrading numerous SharePoint environments to SQL Server 2008 and I have wrestled with system performance. Unless adjustments are made, SQL Server will attempt to consume more than its share of processor. I've seen this cause SharePoint web applications to freeze and become unusable.
A resource management measure for SQL Server 2008 which I consider to be crucial for SharePoint environments, is outlined below. These steps will limit SQL Server Management Studio and Query Analyzer to 25% processor utilization, and possibly preserve the usability of the SharePoint farm. I strongly recommend these steps for SharePoint environments using SQL Server 2008.
SQL Server 2008 Resource Governor
Steps take from TechNet article:
Integration of SQL Server 2008 and Office SharePoint Server 2007
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc990273.aspx
1. Create a resource pool to limit CPU usage to 25 percent
CREATE RESOURCE POOL poolAdhoc
WITH (MAX_CPU_PERCENT = 25);
2. Create a workload group for ad hoc queries and register it with the new resource pool
CREATE WORKLOAD GROUP groupAdhoc
USING poolAdhoc;
3. Create a function that classifies Management Studio and Query Analyzer as members of the ad hoc group
CREATE FUNCTION adhocQueryClassifier() RETURNS SYSNAME
WITH SCHEMABINDING
AS
BEGIN DECLARE @grp_name AS SYSNAME
IF (APP_NAME() LIKE '%MANAGEMENT STUDIO%')
OR (APP_NAME() LIKE '%QUERY ANALYZER%')
SET @grp_name = 'groupAdhoc'
RETURN @grp_name
END
GO
4. Register the new function with Resource Governor
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR
WITH (CLASSIFIER_FUNCTION= dbo.adhocQueryClassifier);
5. Restart Resource Governor
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR RECONFIGURE;
A resource management measure for SQL Server 2008 which I consider to be crucial for SharePoint environments, is outlined below. These steps will limit SQL Server Management Studio and Query Analyzer to 25% processor utilization, and possibly preserve the usability of the SharePoint farm. I strongly recommend these steps for SharePoint environments using SQL Server 2008.
SQL Server 2008 Resource Governor
Steps take from TechNet article:
Integration of SQL Server 2008 and Office SharePoint Server 2007
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc990273.aspx
1. Create a resource pool to limit CPU usage to 25 percent
CREATE RESOURCE POOL poolAdhoc
WITH (MAX_CPU_PERCENT = 25);
2. Create a workload group for ad hoc queries and register it with the new resource pool
CREATE WORKLOAD GROUP groupAdhoc
USING poolAdhoc;
3. Create a function that classifies Management Studio and Query Analyzer as members of the ad hoc group
CREATE FUNCTION adhocQueryClassifier() RETURNS SYSNAME
WITH SCHEMABINDING
AS
BEGIN DECLARE @grp_name AS SYSNAME
IF (APP_NAME() LIKE '%MANAGEMENT STUDIO%')
OR (APP_NAME() LIKE '%QUERY ANALYZER%')
SET @grp_name = 'groupAdhoc'
RETURN @grp_name
END
GO
4. Register the new function with Resource Governor
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR
WITH (CLASSIFIER_FUNCTION= dbo.adhocQueryClassifier);
5. Restart Resource Governor
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR RECONFIGURE;
Wednesday, September 24, 2008
Links: Microsoft SQL Server 2008
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Product Specifications for SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143287.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143506.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Maximum Number of Processors Supported by the Editions of SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143760.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Memory Supported by the Editions of SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143685.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Maximum Capacity Specifications for SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143432.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Editions and Components of SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms144275.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Features Supported by the Editions of SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc645993.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Using Upgrade Advisor to Prepare for Upgrades
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms144256.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Getting SQL Server Assistance
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms166016.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Planning a SQL Server Installation
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb500442.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Overview of SQL Server Installation
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb500438.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: How to: Install SQL Server 2008 (Setup)
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143219.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: How to: Upgrade to SQL Server 2008 (Setup)
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms144267.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Migrating to SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb677619.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Backward Compatibility
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc280407.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143287.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143506.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Maximum Number of Processors Supported by the Editions of SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143760.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Memory Supported by the Editions of SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143685.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Maximum Capacity Specifications for SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143432.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Editions and Components of SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms144275.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Features Supported by the Editions of SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc645993.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Using Upgrade Advisor to Prepare for Upgrades
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms144256.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Getting SQL Server Assistance
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms166016.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Planning a SQL Server Installation
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb500442.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Overview of SQL Server Installation
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb500438.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: How to: Install SQL Server 2008 (Setup)
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143219.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: How to: Upgrade to SQL Server 2008 (Setup)
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms144267.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Migrating to SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb677619.aspx
MSDN: SQL Server 2008 Books Online: Backward Compatibility
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc280407.aspx
Tuesday, November 21, 2006
SQL Server 2005 install error 70233
While I was installing the SQL Server 2005 Prerequisites I came accross this error:
"Errors occurred during the installation: Beta Components Detected. Error 70233 installing .NET Framework 2.0."
After running the utility provided by the link below, the installation was able to successfully continue http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=47598
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Events / Conferences / User Groups
- AIIM Conference
- Boston Area SharePoint User Group
- Boston Azure User Group
- Collaborate
- DevConnections
- DevIntersection
- Enterprise Search Summit
- Microsoft Build
- Microsoft SharePoint Conference
- Microsoft TechEd
- New England ASP.NET Professionals User Group
- New England Oracle Applications User Group
- Oracle Applications User Group (OAUG)
- Oracle OpenWorld
- PeopleSoft Government Contractor Special Interest Group
- PeopleSoft Southern New England Users Group
- Quest International Users Group
- SharePoint Saturday
- SPTechCon
- SQL PASS
- SQL Saturday
- Startup Weekend




